How Is Proton Gradient Used to Make Atp
This energy can be used to take a molecule from inside the cell and move it out or can help make ATP in a specialized enzyme. It can be harnessed to drive a flagellar motor and it is used to pump Na out of the bacterium via a Na -H antiporter that takes the.
The Proton Gradient A Peek At The Physics Behind Atp Synthesis
Thus most bacteria including the strict anaerobes maintain a proton gradient across their plasma membrane.
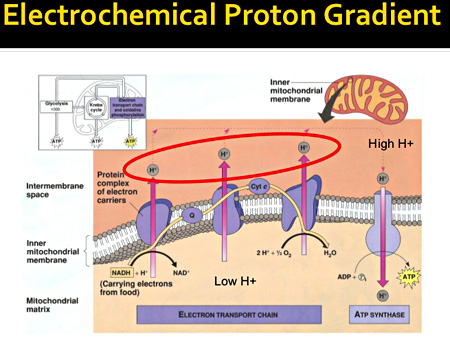
. The production of ATP using energy from the electrochemical gradient is perfected with the evolution of the enzyme ATP synthase found within all life today. ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP using adenosine diphosphate ADP and inorganic phosphate P iIt is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond phosphodiester bond. Proton flow through ATP synthase along a concentration gradient.
The production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation. Proton pumped against the concentration gradient. In bacteria prokaryotes the plasma membrane of the cell is used to provide the proton gradient to produce ATP.
When a hydrogen ion passes down the concentration gradient through a transporter it makes that potential energy available. The change in the solutions pH results in a gradient across the chloroplast membranes such that there is a lower concentration of protons inside the vesicles and a higher concentration outside. During oxidative phosphorylation electrons derived from NADH and FADH 2 combine with O 2 and the energy released from these oxidation reduction reactions is used to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADPThe transfer of electrons from NADH to O 2 is a very energy-yielding reaction with ΔG -525 kcalmol for each pair of electrons transferred.
F1 is a peripheral membrane protein complex having site for synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. F0 is integral membrane protein that form channel for proton. The third complex is composed of cytochrome b.
The energy released during ETC is used to make ATP with the help of ATP synthase which consists of two major parts F1 and F0. Since these electrons bypass and thus do not energize the proton pump in the first complex fewer ATP molecules are made from the FADH 2 electrons. Use of cellular respiration intermediates for biosynthesis.
Oxidative phosphorylation OXPHOS is defined as an electron transfer chain driven by substrate oxidation that is coupled to the synthesis of ATP through an electrochemical transmembrane gradient Figure 131Historically bovine heart mitochondria have been the system of choice for the structural characterization of eukaryotic OXPHOS complexes Saraste 1999 because they. ATP Synthase has two parts. In the same way cell membranes keep the concentration gradient of hydrogen high.
The formation of water molecules. The ATP used for this process is generated by fermentation processes discussed in Chapter 2. The oxidation of FADH2.
This process is related to osmosis the movement of water across a selective membrane which is why it is called chemiosmosis. The part embedded within the membrane of the mitochondria in eukaryotes thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast only in plants or plasma membrane in prokaryotes is called F OThis is a motor that is powered by H ions flowing across the membrane. The Electron Transport Chain.
It is also the. Chemiosmosis is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism. Hydrogen ions or protons will diffuse from a region of high proton concentration to a region of lower proton concentration and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make ATP.
For each ATP produced 2H passes through F0 from the. ATP synthase is a molecular machineThe overall reaction catalyzed by ATP synthase is. The number of ATP molecules ultimately obtained is directly proportional to the number of protons pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
The part within the mitochondria stroma of the chloroplast or inside. The photo-oxidized chlorophyll pigment is then returned to its native state through the splitting of a water molecule which releases molecular oxygen. The oxidation of NADH H.
The proton gradient and the electron transport chain together power the formation of the energy currency of the cell Adenosine Triphosphate ATP. ATP will be produced because the proton gradient favors proton movement through the ATP synthase channels. Many bacteria perform the citric acid cycle too though they do not have mitochondria so the reactions take place in the cytoplasm of bacterial cells.
ATP synthase is a complex molecular machine that uses a proton H gradient to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate Pi. How molecules other than glucose enter cellular respiration. Sir Hans Adolf Krebs a British biochemist is credited with discovering the.

The Electrochemical Proton Gradient And Atp Synthase Learn Science At Scitable
How Is A Proton Gradient Necessary For Atp Generation How Does It Help In The Generation Of Atp During Photosynthesis Quora

Proton Gradients And The Origin Of Life Mother Jones
The Proton Gradient A Peek At The Physics Behind Atp Synthesis
Comments
Post a Comment